Erasure Coding is a technique to achieve strong fault-tolerance in data storage systems. Erasure codes allow fixed number of component failures in overall system with less storage overhead compared to other strategies that can tolerate same number of failures.
Erasure codes are usually specified by two parameters:
n=k+m
- k - original amount of data disks
- m - number of redundant disks added to provide protection from failures
- n - total number of disks after erasure coding process
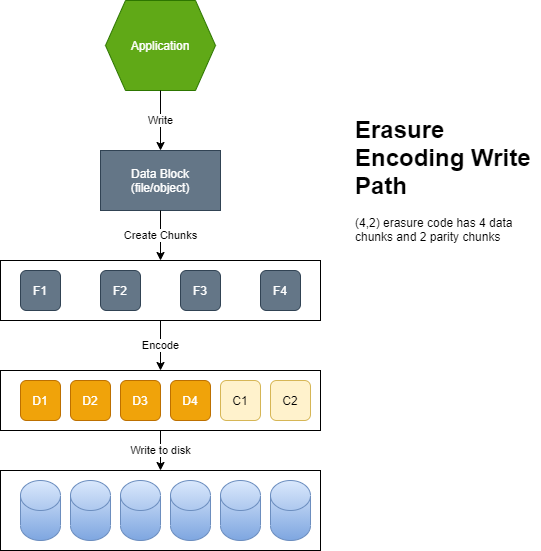
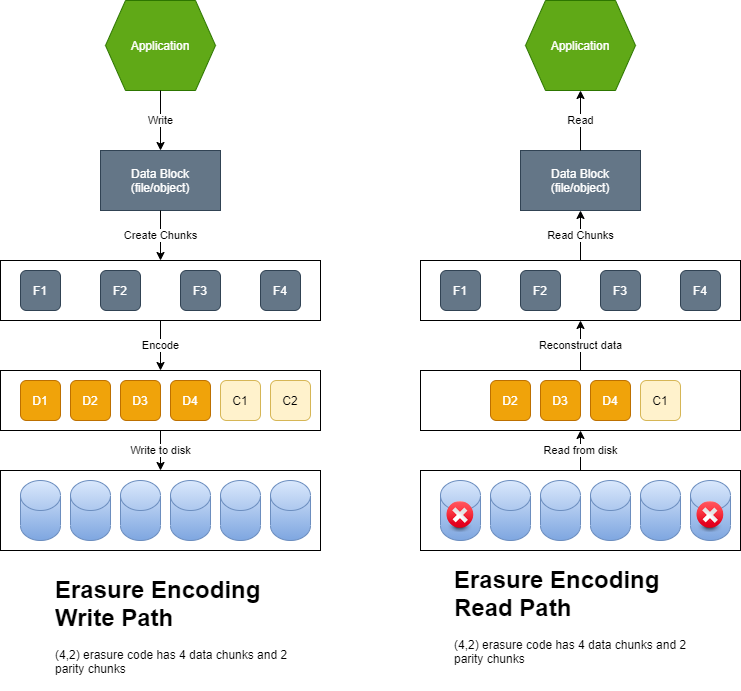
With encoding, the contents of the k data disks are used to calculate the contents of the m coding disks. When up to m disks fail, their contents are decoded from the surviving disks.
As we can see above in the read path, because of maxtrix calculation for data recovery, erasure coding is CPU intensive. Since data needs to be reconstricted from multiple disks, Erasure coding can also be network intensive. Meaning read access can have higher latency.