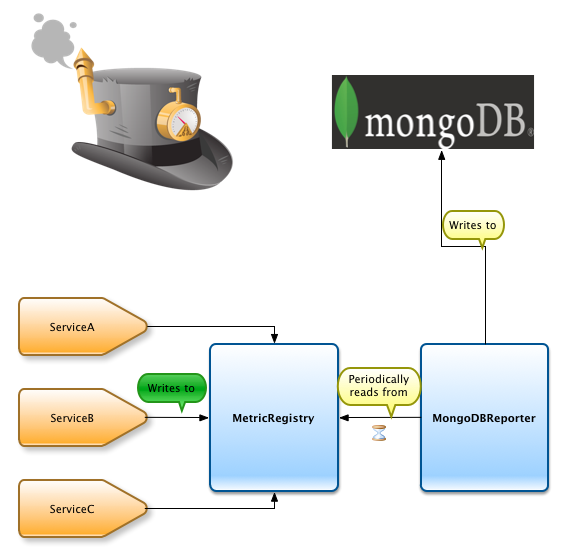
The mongodb-metrics module provides MongoDBReporter, which allows your application to constantly stream metric values to a MongoDB server.
1. Getting Started
The following guide will help you with the first steps towards using the amazing Metrics library with MongoDB reporter.
1.1. Setting Up Maven
Add the following dependency to your project’s Maven POM file.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.aparnachaudhary</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-metrics</artifactId>
<version>${version.mongodb-reporter}</version>
</dependency>
Make sure you have a version.mongodb-reporter property declared in your POM with the current version, which is 0.0.2.
|
This reporter has compile time dependencies towards following libraries:
-
io.dropwizard.metrics:metrics-core:jar:3.1.2
-
org.mongodb:mongo-java-driver:jar:3.1.1
-
org.slf4j:slf4j-api:jar:1.7.13
Note that MongoDB java driver is compatible with 2.4.x, 2.6.x and 3.0.x. So as long as you use one of these versions of MongoDB; you are fine.
1.2. Configuring the reporter
Once you add the maven dependency; next step is to create a registry and configure the reporter with it.
// create metric registry
MetricRegistry metricRegistry = new MetricRegistry();
// configure the reporter
MongoDBReporter reporter = MongoDBReporter.forRegistry(metricRegistry)
.serverAddresses(new ServerAddress[]{new ServerAddress("192.168.99.100", 32768)}) (1)
.withDatabaseName("javasedemo") (2)
.prefixedWith("javase") (3)
.build();
// Report metrics every 5 seconds to MongoDB
reporter.start(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);| 1 | MongoDB connection details |
| 2 | Name of the database in MongoDB |
| 3 | Prefixes the metrics that are reported with the given identifier |
Now that we have configured the registry and the reporter; next step is to perform some instrumentation. For the demo, we use a simple metric counter. A counter is just a counter. You can increment or decrement its value. You can use it, for instance, for counting the number of requests made to a particular HTTP endpoint.
// register metric
metricRegistry.counter("demo.counter");
// sleep for 10 seconds so that metric is reported to MongoDB store
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}Executing the above program creates a collection counter in javasedemo database.
Counter collection:
/* 0 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("565b3b7ec8f3530f3a327001"),
"name" : "javase.demo.counter",
"count" : 1,
"timestamp" : ISODate("2015-11-29T17:53:02Z")
}
/* 1 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("565b3b83c8f3530f3a327005"),
"name" : "javase.demo.counter",
"count" : 1,
"timestamp" : ISODate("2015-11-29T17:53:07Z")
}